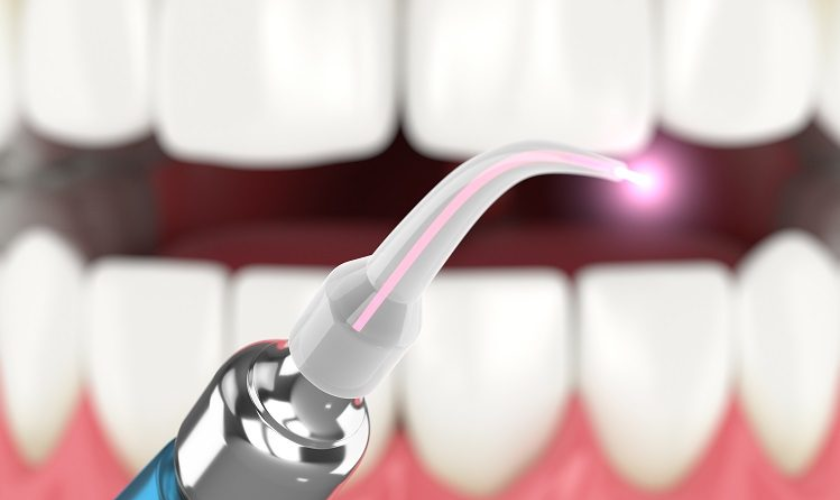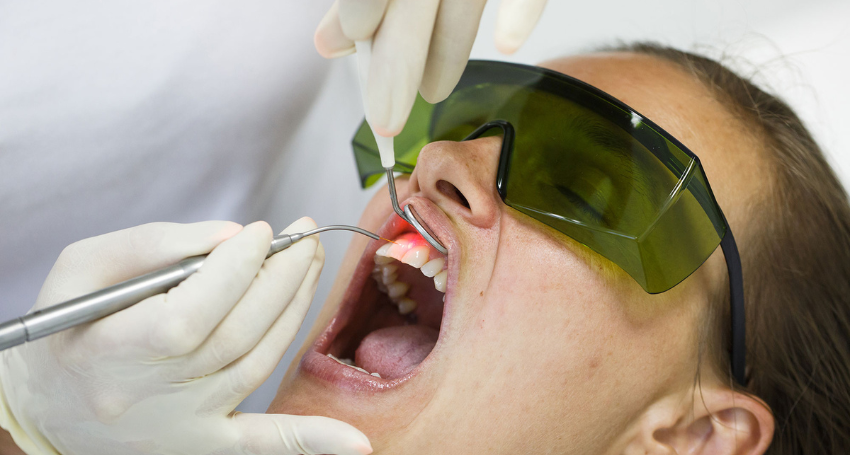
Let’s explain if your dentist has talked to you about LANAP and you’re wondering what it is. LANAP, or Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure, is a modern and minimally invasive way to treat gum disease. Instead of traditional surgery that involves cutting and stitching, LANAP protocol uses a laser to target and remove only the damaged gum tissue, leaving the healthy tissue untouched. It’s a more comfortable option for treating periodontal disease and can make a big difference in your recovery.
How Does LANAP Work?
LANAP uses a laser to get into the deep pockets around your teeth, where gum disease hides out. The laser carefully cleans out the bacteria and infected tissue while leaving the healthy gums alone. This precision means you don’t lose healthy gum tissue, which is a big plus compared to traditional surgery.
The best part? The laser removes the bad stuff and encourages bone and tissue regeneration. That’s right—it helps your mouth heal by promoting tissue regrowth that may have been lost due to the disease. Plus, because the laser sterilizes the area, it lowers the risk of infection and helps you heal faster.
Why LANAP?
LANAP has some great benefits that make it worth considering if you’re dealing with gum disease. Let’s go through some of the key reasons patients choose LANAP:
- Minimally Invasive: The LANAP procedure doesn’t involve any cutting or stitching, so it’s gentler on your gums. Most patients experience little to no discomfort during and after the procedure.
- Preserve Healthy Gum Tissue: The laser only targets the diseased tissue, so your healthy gums stay intact. This means less gum recession, and your smile will stay natural.
- Stimulates Healing: it actually helps your body heal by encouraging the regrowth of bone and tissue around your teeth. This can help save teeth that might otherwise need to be extracted due to gum disease.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Because the laser sterilizes the area as it works, there’s a reduced chance of infection compared to traditional surgery.
- Quick Recovery: Since it is less invasive, you’ll likely recover faster than you would with traditional surgery. Most patients are back to their normal routine quickly, with minimal downtime.
Pros and Cons
LANAP is a great option for many patients, but as with any treatment, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons.
Pros:
- Less Pain and Discomfort: It is much less painful than traditional gum surgery, and most patients report little to no discomfort during the procedure.
- Faster Recovery: Without stitches, recovery is quicker, and there’s less risk of complications.
- Preserve Healthy Gum Tissue: Only diseased tissue is removed, keeping your healthy gums in place.
- Encourages Bone Regrowth: It helps promote bone and gum tissue regrowth, improving long-term oral health.
- Lower Infection Risk: The laser sterilizes the treatment area, reducing the risk of post-procedure infection.
Cons:
- Availability: Not all dentists are trained in LANAP, so you may need to find a specialist.
- Cost: LANAP can be more expensive than traditional gum surgery, mainly due to the advanced laser technology involved.
- Effectiveness Depends on Gum Disease Stage: LANAP works best in certain stages of gum disease, so it may not be suitable for everyone.
Is LANAP Right for You?
LANAP is a great option for those looking for a less invasive treatment for gum disease. It’s especially useful if you’re hoping to avoid the discomfort and longer recovery times that come with traditional surgery. However, since LANAP isn’t offered by all dentists and might cost more, it’s worth conversing with your dental provider to see if it’s the best fit for your specific situation.
If you want to learn more about LANAP and how it could help you, call us today! We’d happily schedule a consultation and walk you through your treatment options. Your smile deserves the best care, and we’re here to help you make the right choice for your health.